Understanding Diabetes Types: A Complete Guide to Symptoms, Causes, and Management
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. With rising prevalence globally, understanding the diabetes types is critical for effective diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), over 537 million adults worldwide were living with diabetes in 2021—a number expected to reach 643 million by 2030. These numbers highlight the need for awareness about the different types of diabetes, how they differ, and how to manage them effectively.
There are several diabetes types, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatments. However, they all share the common issue of elevated blood glucose levels, also known as hyperglycemia. Learning about the specific type of diabetes helps patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about lifestyle, medication, and long-term care.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose (sugar), which enters the bloodstream. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps move glucose from the blood into cells to be used for energy.
In people with diabetes, the body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use it properly. This results in excess glucose remaining in the blood, leading to potential damage to the heart, kidneys, nerves, eyes, and other organs if not managed appropriately.
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, previously known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, teens, or young adults but can occur at any age.
Symptoms:
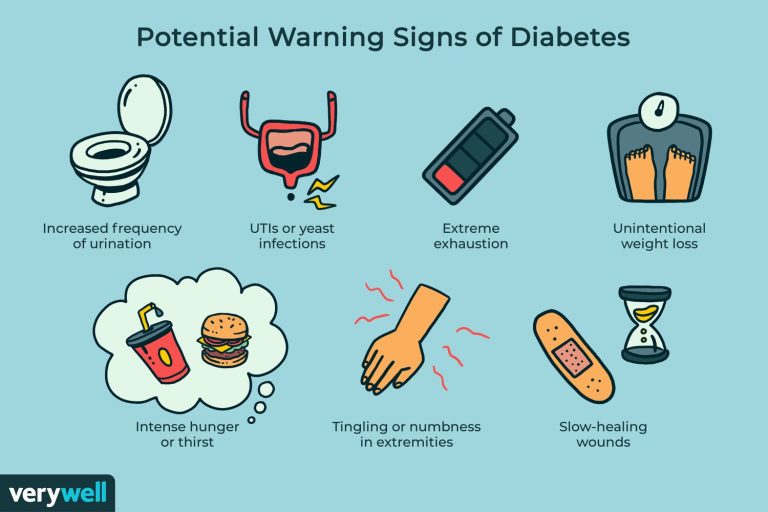
- Increased thirst and urination
- Sudden weight loss
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Causes:
- Autoimmune reaction
- Genetic predisposition
- Environmental triggers (e.g., viruses)
Treatment:
- Daily insulin injections or insulin pump
- Blood sugar monitoring
- Carbohydrate counting
- Healthy eating and regular physical activity
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for over 90% of cases globally. It typically develops in adults over age 45, but increasing numbers of children and young adults are being diagnosed due to rising obesity rates.
In this condition, the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
Symptoms:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Slow healing of wounds
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Frequent infections
- Fatigue and blurry vision
Causes:
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Poor diet
- Family history of diabetes
- Ethnic background
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise)
- Oral medications (e.g., metformin)
- Injectable medications
- Insulin therapy (in advanced cases)
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased needs of both mother and baby. It usually develops around the 24th to 28th week and disappears after delivery, although it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later.
Symptoms:
- Often no symptoms
- Increased thirst and urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
Risk Factors:
- Being overweight or obese
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Age over 25
- Previous gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Treatment:
- Meal planning and exercise
- Blood sugar monitoring
- Insulin therapy if needed
4. Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. It’s a critical warning sign that shouldn’t be ignored. According to the CDC, more than 96 million adults in the U.S. have prediabetes, but over 80% don’t know they have it.
Symptoms:
- Often asymptomatic
- May experience darkened skin on neck, armpits, or elbows (acanthosis nigricans)
Causes:
- Insulin resistance
- Poor dietary habits
- Sedentary lifestyle
Prevention and Management:
- Weight loss
- Regular exercise
- Healthy diet
- Regular monitoring
5. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
MODY is a rare form of diabetes that typically occurs before age 25 and is caused by a genetic mutation. Unlike type 1 or type 2, MODY is not autoimmune or linked to lifestyle factors. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
Symptoms:
- Mild elevation in blood sugar
- Often misdiagnosed as type 1 or 2 diabetes
Treatment:
- Often managed with oral medications
- Some types may not require insulin
6. Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus (NDM)
NDM is a rare form of diabetes that occurs in the first 6 months of life. It can be transient (temporary) or permanent.
Symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Dehydration
- Failure to thrive
Causes:
- Genetic mutations affecting insulin production
Treatment:
- Insulin or sulfonylureas, depending on genetic testing results
7. Secondary Diabetes
Secondary diabetes develops as a result of another medical condition or due to medications. Conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or pancreatitis, or the use of steroids or chemotherapy, can cause secondary diabetes.
Symptoms and treatment are similar to type 2 diabetes but are managed by treating the underlying condition alongside standard diabetes care.
Key Differences Between Diabetes Types
| Type | Cause | Insulin Dependency | Age Group | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Autoimmune | Yes | Children, Young Adults | No |
| Type 2 | Insulin Resistance | Sometimes | Adults (also rising in youth) | Sometimes (with lifestyle) |
| Gestational | Pregnancy Hormones | Sometimes | Pregnant Women | Often after childbirth |
| Prediabetes | Insulin Resistance | No | Adults | Yes (with lifestyle) |
| MODY | Genetic Mutation | Sometimes | Youth < 25 | Depends on subtype |
| NDM | Genetic Mutation | Yes | Infants | Sometimes |
Why Early Detection Matters
Early diagnosis of any diabetes type is crucial to prevent serious complications like cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. Routine screening, especially for those at risk, can detect prediabetes or type 2 diabetes before symptoms develop.
How to Get Diagnosed
Doctors use the following tests to diagnose different types of diabetes:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test
- HbA1c Test (average blood glucose over 2-3 months)
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (especially for gestational diabetes)
- Random Blood Sugar Test
- Genetic testing (for MODY or NDM)
Living with Diabetes: Daily Management Tips
- Follow a diabetes-friendly diet rich in fiber and low in refined carbs
- Engage in regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes per week)
- Monitor blood sugar levels as recommended
- Take medications or insulin as prescribed
- Manage stress through mindfulness, yoga, or therapy
- Stay updated on vaccinations and routine check-ups
The Future of Diabetes Treatment
Advances in diabetes management are rapidly evolving. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), insulin pumps, and even smart insulin pens are making self-care more convenient. Research into beta-cell regeneration, stem cell therapy, and immunotherapy for type 1 diabetes offers promising possibilities.
Conclusion
Understanding the diabetes types is the first step in managing the condition effectively. Whether it’s type 1, type 2, gestational diabetes, or a rare form like MODY, early diagnosis and the right care plan can make a significant difference in quality of life. With rising diabetes rates globally, awareness, education, and regular check-ups are more important than ever.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of diabetes?
The main types are type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and prediabetes. Less common types include MODY, NDM, and secondary diabetes.
2. What is the most common type of diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is the most common, accounting for over 90% of all diabetes cases worldwide.
3. Can type 2 diabetes be reversed?
Yes, in some cases, type 2 diabetes can be reversed through weight loss, diet, and lifestyle changes, especially when diagnosed early.
4. How is type 1 diabetes different from type 2?
Type 1 is an autoimmune disease requiring insulin from diagnosis. Type 2 is often lifestyle-related and may not require insulin initially.
5. What is gestational diabetes?
It’s a form of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth but increases the risk of type 2 later in life.
6. How do I know if I have prediabetes?
Prediabetes usually has no symptoms. A blood test measuring fasting glucose or HbA1c is needed for diagnosis.
7. Is diabetes genetic?
Genetics can play a role, especially in type 2 and MODY. However, lifestyle and environmental factors also contribute.
8. What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Common symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds.
9. What tests are used to diagnose diabetes?
Common tests include fasting blood glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, HbA1c, and genetic tests for rare forms.
10. Can children get diabetes?
Yes, children can develop type 1 diabetes and, increasingly, type 2 due to rising obesity rates.