What Are 10 Warning Signs of Diabetes? Early Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, and its early detection can significantly influence how effectively it’s managed. But many people don’t realize they have diabetes until complications begin to appear. This makes it crucial to understand what are 10 warning signs of diabetes, so you can identify them early and seek medical intervention before it becomes more serious. Whether it’s type 1, type 2, or prediabetes, early symptoms often overlap and provide key signals your body needs help regulating blood sugar.
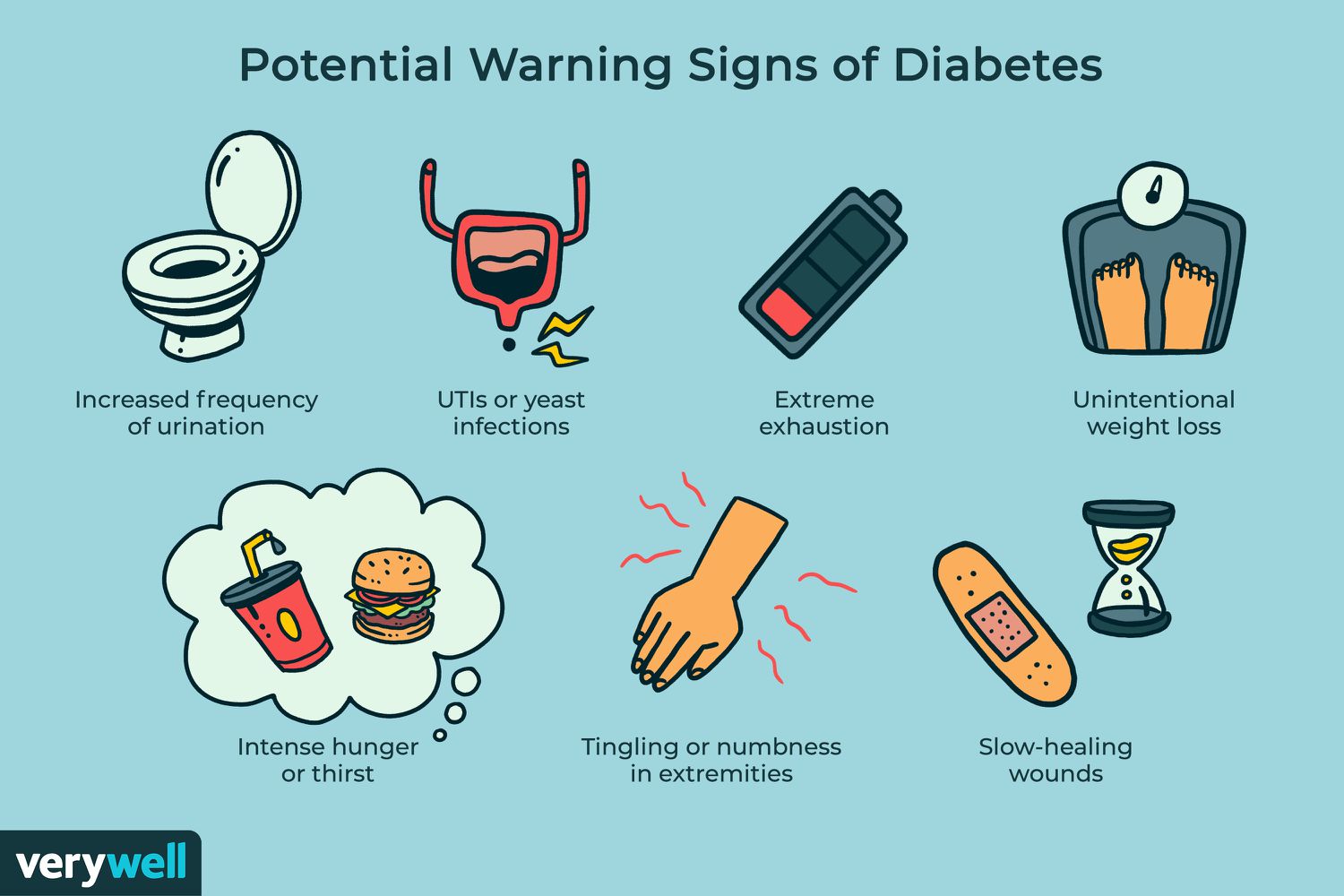
1. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
One of the earliest signs of diabetes is increased urination. When blood sugar levels are too high, the kidneys work overtime to filter and absorb the excess glucose. The glucose that can’t be absorbed is excreted in the urine, which pulls fluids from your tissues. This leads to frequent urination, often waking individuals up at night to use the bathroom.
2. Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia)
Frequent urination can lead to dehydration. In response, your body signals the need for more fluids, causing persistent thirst. This thirst doesn’t go away even after drinking plenty of water. Polydipsia is especially prominent in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and should not be ignored if it persists.
3. Extreme Hunger (Polyphagia)
High blood sugar can interfere with your body’s ability to convert glucose into energy. When cells don’t get the energy they need, they signal the brain to increase food intake. This leads to a constant feeling of hunger, even after eating. Polyphagia is a key sign that the body isn’t using insulin properly.
4. Unexplained Weight Loss
Despite eating more, many people with undiagnosed diabetes experience weight loss. This is because the body begins burning muscle and fat for energy when it can’t access glucose. In type 1 diabetes, this symptom can occur rapidly, while in type 2, it may develop gradually. Losing 10 pounds or more without changes in diet or exercise should be a red flag.
5. Fatigue and Weakness
When your cells lack glucose, your body becomes tired and sluggish. Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms of diabetes and often goes unnoticed or is attributed to stress or lack of sleep. Persistent tiredness, even after rest, could be a sign your blood sugar is not well controlled.
6. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar can cause swelling in the lenses of your eyes by drawing fluid from surrounding tissues, including the lenses. This changes the shape and flexibility of the lens, leading to blurred vision. If untreated, high glucose levels can cause long-term damage to the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy.
7. Slow Healing of Cuts and Wounds
Elevated blood glucose levels can impair blood circulation and damage blood vessels, which slows the healing process. Even minor cuts, scrapes, or infections may take weeks to heal. This delay can also increase the risk of infection and is especially dangerous for wounds on the feet and legs.
Also Read: Can Diabetics Eat Onion Rings? A Complete Guide to This Crispy Dilemma
8. Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet (Neuropathy)
Diabetes can damage nerves, especially in the extremities. This is known as diabetic neuropathy and typically starts with tingling, numbness, or burning sensations in the hands or feet. Left untreated, it can lead to loss of feeling, muscle weakness, or even ulcers and amputations in severe cases.
9. Dark Patches of Skin (Acanthosis Nigricans)
One visible sign of insulin resistance is the appearance of dark, velvety patches of skin, often in the neck, armpits, elbows, or groin. This condition, known as acanthosis nigricans, is common in people at risk of type 2 diabetes and is often seen in obese individuals.
10. Frequent Infections
High blood sugar can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections. Diabetics may experience frequent urinary tract infections, yeast infections, gum disease, or skin infections. These infections may also take longer to clear up than normal.
The Importance of Recognizing These Symptoms Early
Identifying the early warning signs of diabetes can help individuals get diagnosed before serious complications arise. Type 2 diabetes, in particular, develops gradually and can go unnoticed for years. According to the CDC, over 8 million Americans are living with undiagnosed diabetes. Early detection allows for better management and a lower risk of developing issues like cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and vision problems.
Who is at Risk of Developing Diabetes?
Certain factors increase your risk of developing diabetes. These include:
- Family history of diabetes
- Obesity or being overweight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- High blood pressure or cholesterol
- History of gestational diabetes
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
People with multiple risk factors should be especially vigilant about these early signs.
What to Do if You Notice the Symptoms
If you experience any of these warning signs, especially in combination, consult your doctor immediately. A simple blood test such as fasting glucose or A1C can help determine if you have diabetes or are at risk.
Early diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment, lifestyle changes, and possibly even reversing prediabetes through weight loss, diet, and exercise.
Living with Diabetes: Long-Term Management
Once diagnosed, managing diabetes involves lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medication or insulin therapy. Key components of diabetic care include:
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Following a balanced diet low in processed carbs and sugar
- Staying physically active
- Managing stress
- Getting regular check-ups
Support from diabetes educators, dietitians, and healthcare providers plays an essential role in achieving stable blood sugar levels and reducing long-term complications.
When Symptoms Are a Sign of Diabetic Complications
Ignoring early symptoms can lead to complications like:
- Diabetic retinopathy (eye damage)
- Kidney disease (nephropathy)
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Foot problems and amputations
The earlier diabetes is diagnosed, the better the outcome. If symptoms are worsening or new symptoms appear, it may indicate complications requiring urgent medical attention.
Also Read: Onion Rings and Diabetes: Can You Eat Them Without Spiking Blood Sugar?
Conclusion
Understanding what are 10 warning signs of diabetes can help you detect the disease early, start treatment, and avoid serious health issues. These symptoms—frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme hunger, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, numbness, skin changes, and frequent infections—are your body’s way of signaling that something is wrong. If you or someone you know is experiencing multiple symptoms, consult a healthcare provider and get tested. Early detection can mean the difference between a manageable condition and life-threatening complications. Make awareness and proactive health screening a priority in preventing the silent progression of diabetes.
FAQs
1. What are the first warning signs of diabetes?
Increased urination, excessive thirst, and unexplained fatigue are often the earliest signs.
2. Can diabetes symptoms come on suddenly?
Yes, particularly in type 1 diabetes, symptoms can develop rapidly over days or weeks.
3. Is blurred vision always a sign of diabetes?
Not always, but it can be caused by high blood sugar affecting the eyes. Persistent blurry vision should be checked.
4. What type of diabetes shows no symptoms?
Type 2 diabetes often has no obvious symptoms in the early stages.
5. How long can you have diabetes without knowing?
Some people live with undiagnosed diabetes for years, especially type 2.
6. Are skin changes a sign of diabetes?
Yes, dark patches (acanthosis nigricans) are common in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
7. Is frequent urination at night a diabetes symptom?
Yes, high blood sugar can lead to nighttime urination, known as nocturia.
8. Can diabetes cause tingling in feet?
Yes, tingling or numbness in feet is a common symptom of diabetic neuropathy.
9. What should I do if I have multiple symptoms?
See your doctor for a blood test to check glucose or A1C levels.
10. Can early diabetes symptoms be reversed?
In prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes, symptoms can improve or reverse with lifestyle changes and medical support.